Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that has garnered increasing attention, especially as this demographic faces heightened risks. Individuals aged 75 and older experience the highest rates of suicide among any age group, yet resources designed specifically for them are alarmingly sparse. Recent research underscores the direct link between mental health in the elderly and factors such as loneliness, which significantly contributes to their vulnerability. Addressing the unique challenges of aging and mental health requires an urgent strategy to equip seniors with accessible resources for suicide prevention. By leveraging insights from geriatric psychiatry, we can develop targeted interventions to mitigate these risks and provide vital support for our aging population.
Preventing suicide among seniors is an urgent public health concern that needs to be addressed with compassion and understanding. Elders, particularly those experiencing severe isolation, are at a distinct risk of mental health issues, including suicidal tendencies. This topic is intertwined with discussions on wellbeing in later life, highlighting the importance of creating tailored interventions that address the specific needs of this population. Incorporating informed strategies that focus on senior mental wellness can significantly impact loneliness and related suicide risks. As we continue to explore effective methods to support older adults, recognizing their unique challenges is key to fostering a healthier environment.
Understanding the Suicide Crisis Among Older Adults
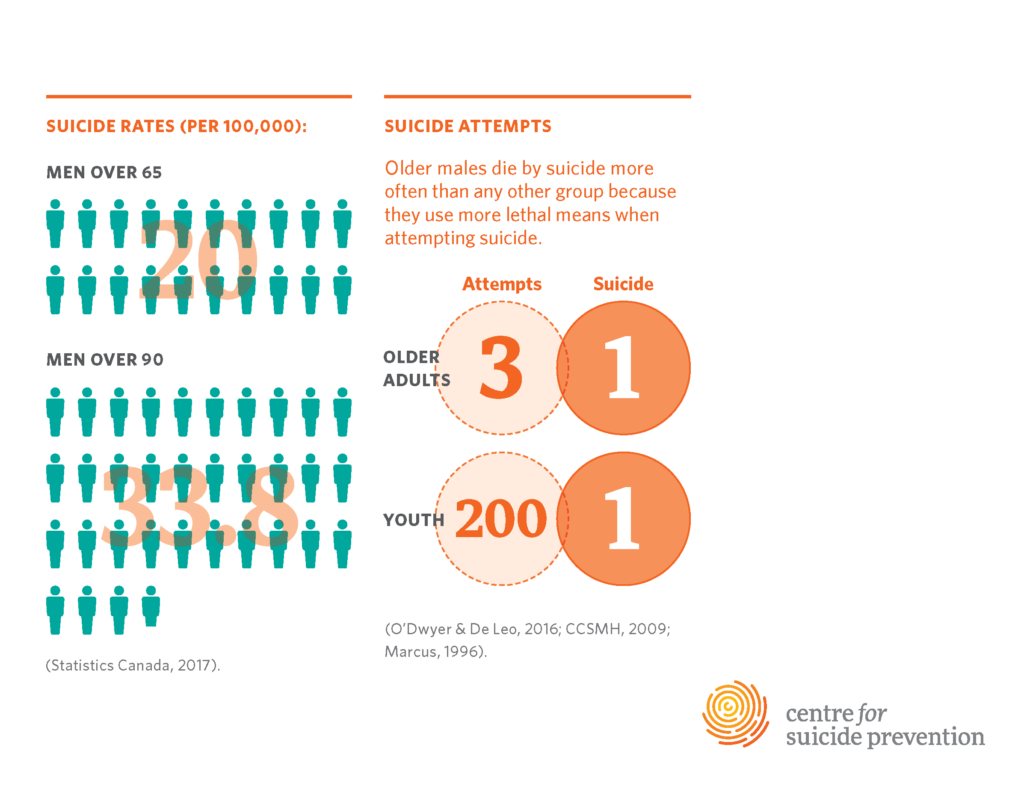
Older adults, particularly those aged 75 and above, represent a disproportionate demographic in suicide statistics, indicating the gravitas of this crisis. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlights that older adults have a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000, underscoring an urgent public health concern. Research in geriatric psychiatry reveals that loneliness and social isolation are significant contributors to suicidal ideation among the elderly. Many older adults struggle with feelings of abandonment or depression, exacerbated by the loss of loved ones and the challenges of aging that are not often addressed in mainstream mental health discussions.
Despite this alarming trend, existing resources for suicide prevention and mental health care for seniors are scant. Major national organizations, while acknowledging the rising suicide rates among older adults, fail to actively provide them with accessible information and support tailored to their unique needs. This imbalance reinforces the isolation these individuals may already feel, making it crucial to not only recognize their plight but also mobilize targeted efforts to mitigate the risk of suicide in this vulnerable population.
The Importance of Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Suicide prevention for older adults is not only necessary; it is vital. Addressing mental health in the elderly requires a comprehensive understanding of the emotional and psychological challenges they face. Factors such as chronic illness, loss of social networks, and mental health stigma can all contribute to a decline in an older adult’s well-being. Programs specifically aimed at engaging this demographic are essential for reducing the risks associated with loneliness and mental health deterioration. Moreover, investing in geriatric psychiatry initiatives could significantly improve the accessibility and effectiveness of mental health resources for seniors.
To effectively tackle suicide prevention in this age group, strategies must be implemented that acknowledge their unique experiences. Tailored campaigns can help spread awareness and provide education on available resources, emphasizing the importance of community support and proactivity in seeking help. Additionally, building supportive networks involving family members and caregivers can create a more nurturing environment that encourages older adults to express their feelings and seek help when needed.
Resources for Senior Suicide Prevention: Meeting the Need
Older adults must have access to resources specifically designed for their suicide prevention strategies. The needs of seniors differ significantly from those of younger populations, necessitating comprehensive and targeted support efforts. Currently, successful loneliness interventions and preventative mental health programs are often overlooked for this age group. By collaborating with community organizations, healthcare systems, and mental health advocates, we can bridge the resource gap that currently exists and ensure that seniors receive the care and attention they deserve.
Geriatric psychiatry offers a pathway towards understanding and addressing the complex mental health needs of older adults. It serves as an essential component in the formation of programs that not only promote awareness about mental health issues like depression and anxiety but also encourage those at risk to consider seeking help. By prioritizing the development of resources explicitly aligned with seniors, we can tackle the dire issue of elderly suicide and foster a healthier, more engaged aging community.
The Consequences of Loneliness and Suicide Risk in the Elderly
Loneliness is often cited as a significant risk factor for suicide among older adults, underscoring the urgent need for action against this silent epidemic. As family members pass away and friends become scarce, many elderly individuals find themselves isolated with their feelings of despair. This emotional isolation can lead to a downward spiral, where the lack of social support aggressively contributes to mental health issues, including depression, exacerbating their overall vulnerability when it comes to suicidal thoughts.
Interventions focused on reducing feelings of loneliness through community engagement can greatly alleviate suicide risk. Programs such as outreach initiatives and support groups designed for older adults emphasize building social connections that can combat the pervasive sense of isolation. By fostering social bonds and providing opportunities for personal connection, we can create a supportive environment that encourages conversations around mental health and suicide prevention.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Addressing Senior Mental Health
Healthcare providers play an essential role in promoting mental health awareness among older adults. Training programs in geriatric psychiatry should emphasize the identification of risk factors and signs of mental health issues associated with suicide. Creating a safe space for older patients to express concerns about their mental well-being allows healthcare providers to facilitate appropriate interventions and resources. Moreover, regular mental health assessments within typical healthcare visits can ensure that issues are addressed holistically.
Further, it is vital for healthcare practitioners to collaborate with community organizations and mental health services to enhance resource accessibility for their older patients. Awareness-building campaigns geared towards senior health programs can arm providers with more robust tools for patient education, empowering elderly individuals to take ownership of their mental well-being and enabling them to seek help when needed.
Advocating for Increased Research and Funding in Geriatric Mental Health
Increasing funding and research focused on late-life suicide prevention is of paramount importance as the population of older adults continues to rise. Allocating resources towards identifying best practices in geriatric mental health can enhance our understanding of the complexities surrounding aging, loneliness, and mental illness. By prioritizing research in these areas, we can develop evidence-based strategies that promote effective interventions tailored to the needs of older adults.
Advocacy for better funding in geriatrics can lead to the implementation of vital programs that address the alarming rates of suicide in older demographics. It is imperative for policymakers to recognize the necessity for long-term commitments that fortify mental health resources for seniors, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and care. By championing the unique experiences of older adults and highlighting their contributions, we can foster an environment that values their mental health needs and actively works to protect them from the risks of suicide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective resources for suicide prevention for older adults?
Effective resources for suicide prevention for older adults encompass various strategies, including hotlines specifically designed for seniors, community outreach programs, and online platforms that offer mental health support tailored to their unique needs. Organizations like the National Institute of Mental Health and local geriatric psychiatry clinics provide information and resources to aid in mental health for elderly populations.
How does loneliness increase suicide risk in older adults?
Loneliness significantly increases suicide risk in older adults due to feelings of isolation, despair, and lack of support systems. Research shows that social isolation can exacerbate mental health issues, making it crucial to address loneliness through engagement in community activities and programs that foster social connections.
What role does geriatric psychiatry play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a vital role in suicide prevention for older adults by diagnosing and treating mental health issues that may contribute to suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Specialists in this field focus on the unique healthcare needs of the elderly, providing tailored interventions that address both psychological and social factors.
Why is suicide prevention for older adults often overlooked?
Suicide prevention for older adults is often overlooked due to a lack of awareness regarding the high rates of suicide in this age group and systemic biases that diminish the visibility of senior mental health issues. This discrepancy calls for more public-facing campaigns that specifically target older adults and their unique circumstances.
What can families do to support suicide prevention for older adults?
Families can support suicide prevention for older adults by fostering open communication, encouraging social interaction, and being vigilant about signs of depression or isolation. They can also assist in finding appropriate mental health resources and support organizations that specialize in elderly mental health.
How can community programs help in mental health for elderly populations?
Community programs can greatly enhance mental health for elderly populations by providing social support, recreational activities, and direct access to mental health services. These programs can help combat isolation and promote a sense of belonging, which are crucial for preventing suicide among older adults.
What signs should caregivers look for in older adults at risk of suicide?
Caregivers should look for signs such as withdrawal from social activities, noticeable changes in mood or behavior, expressions of hopelessness, and any discussions about death or suicide. Early identification of these signs can facilitate timely intervention and support.
What research is being conducted on aging and mental health in relation to suicide prevention?
Current research on aging and mental health concerning suicide prevention focuses on understanding the specific health needs of older adults, identifying risk factors, and developing interventions. Studies aim to highlight disparities in mental health services for seniors, seeking funding and awareness to address these critical issues.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Older adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates, but lack adequate resources for prevention efforts. |
| National suicide prevention organizations do not effectively target older adults, despite acknowledging their high risk. |
| A study by McLean Hospital indicates a significant imbalance in online suicide prevention resource availability for seniors. |
| Social isolation, underrepresentation in research, and implicit biases contribute to the rising suicide rates among older adults. |
| There is an urgent need for tailored campaigns and resources focusing on the unique healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Increased funding and research for late-life suicide prevention are critical for addressing this public health issue. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical concern, as this demographic faces the highest suicide rates among age groups. Despite this alarming statistic, existing resources are insufficient and poorly targeted to meet their needs. To effectively combat this issue, more accessible and tailored suicide prevention campaigns must be developed, ensuring older adults receive the support necessary to prevent isolation and loneliness, which contribute to their vulnerability. Enhanced research and funding focused specifically on older populations will be essential to bridge these gaps in care.